What is Lupus?
Written by Sai Koppada
Introduction
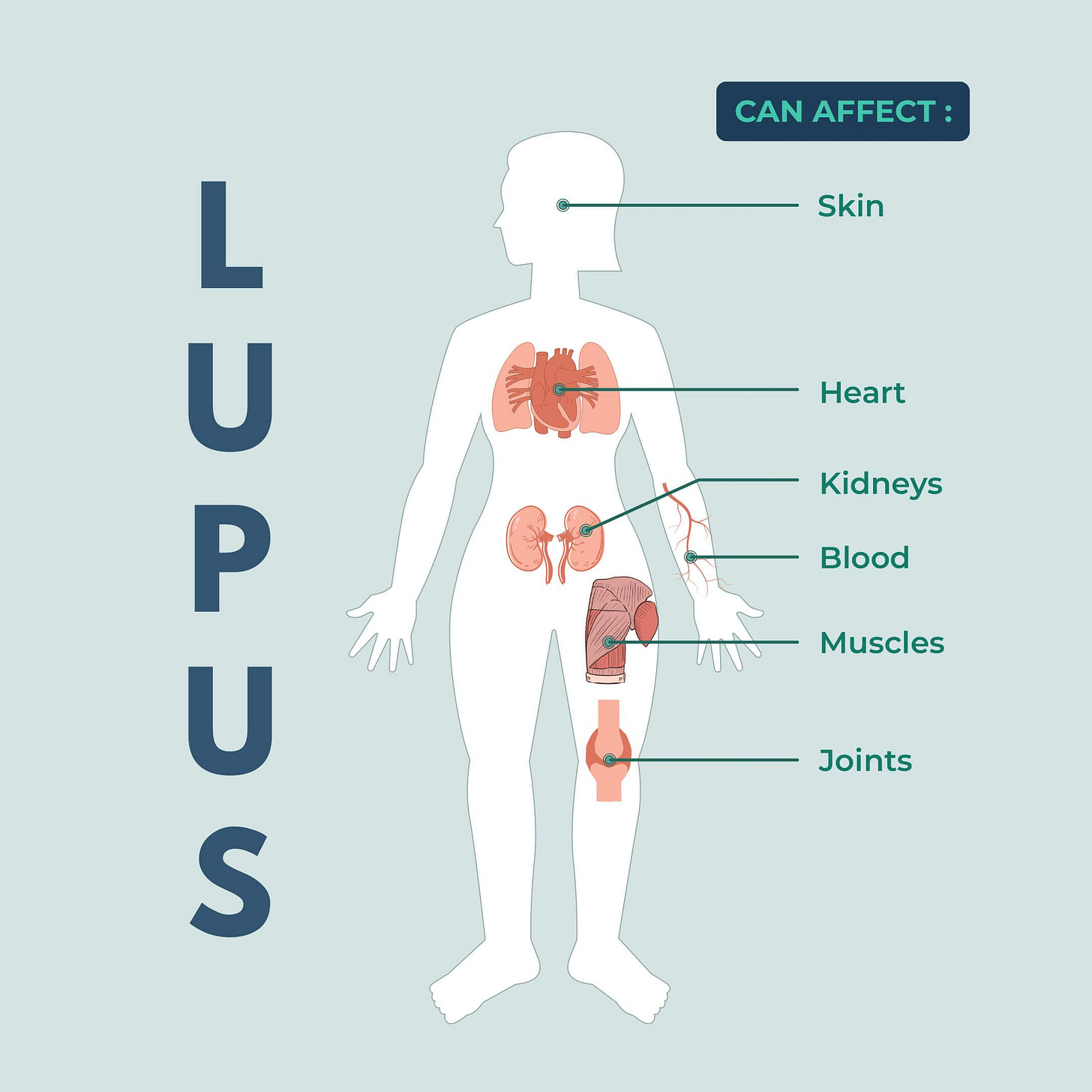
Lupus, also known as systemic lupus erythematosus, is an autoimmune disorder that affects multiple organs within the body. This autoimmune condition in particular affects multiple parts of the body including the skin, joints, kidneys, and lungs so identifying and diagnosing this condition can be a challenge. This is a condition where the immune system mistakes healthy cells within the body for infected ones and attacks them, leading to inflammation and pain within the body. The symptoms of this condition can vary from person to person, making it hard to effectively administer treatment for the patient.
Causes
Though the exact cause of Lupus is unknown, a variety of factors can contribute to the development of this condition. Factors such as genetics, the environment, and hormonal imbalances within the body can all contribute to the development of Lupus. When a person has a familial history of the condition, they are more likely to inherit the specific genetic sequence that causes the condition. Additionally, exposure to certain infections and pathogens can cause the development of Lupus. Hormonal imbalances, particularly in women, can also cause the disease to worsen and cause discomfort.
Symptoms
Since this type of autoimmune disorder can cause a range of symptoms, it can make it very difficult to properly diagnose and treat the condition. However, some of the common symptoms of Lupus include skin rashes, joint pain, fatigue, fever, kidney problems, swelling, increased skin sensitivity, and shortness of breath. The immune system wrongly attacks healthy cells in the body causing inflammation throughout the body, leading to different severity of these symptoms. The inflammation can lead to severe amounts of pain and discomfort for an individual. In certain cases the immune system can attack healthy cells that are located in specific organs such as the kidney and skin causing irritation and disrupting the function of those organs; this causes symptoms such as kidney failure and skin rashes.
Diagnosis
The primary methods of diagnosis for this condition are physical examinations, antibody tests, DNA tests (anti-dsDNA), blood count tests, imaging scans, and biopsies. Physical examinations and medical histories are used to check for symptoms such as rashes and inflammation. Blood tests and DNA tests are used tests for common symptoms of Lupus such as low white blood count, protein in the urine, and specific antibodies. These tests however may be misleading because the presence of certain antibodies or protein may not be present in the tests even if the person has Lupus. Imaging scans are also used to assess inflammation in the body, and biopsies are used to examine the body for tissue damage and assess the state of the organs.
Treatment
Common treatments used to treat lupus are Anti-inflammatory drugs, antimalarials, immunosuppressants, and corticosteroids. Though there is no cure for the condition, these treatments are used to help relieve some of the pain, reduce inflammation, prevent flare-ups of skin rashes, and reduce the activity in the immune system so that it stops attacking healthy cells. Along with this, lifestyle changes are also used as treatments to prevent skin irritation and reduce some of the symptoms associated with Lupus. These lifestyle changes include using appropriate sun protection, maintaining a balanced diet, and engaging in regular exercise. In addition, various treatments and medications may be prescribed based on the severity of the symptoms to effectively manage the condition.
Understanding the cause of the condition and recognizing its symptoms can help individuals seek appropriate treatment early. It can also help them identify and treat the disease before it becomes too severe.
References
“How Lupus Affects the Body.” Lupus Foundation of America, 2024, www.lupus.org/resources/how-lupus-affects-the-body?utm_source=bing&utm_medium=cpc&utm_campaign=Search%3A%20NRCL&utm_term=of%20lupus&utm_id=. Accessed 11 Aug. 2024.
“A Treatment Option | BENLYSTA (Belimumab).” Benlysta.com, 2022, www.benlysta.com/what-is-lupus/?cc=ps_V0MO6RSQ1N1272718&mcm=60004&&msclkid=568c9d9152ad110fd835fb294c974e44&gclid=568c9d9152ad110fd835fb294c974e44&gclsrc=3p.ds. Accessed 11 Aug. 2024.
Written by Sai Koppada from MEDILOQUY