Pneumonia
Written by Darshana Srivatsan
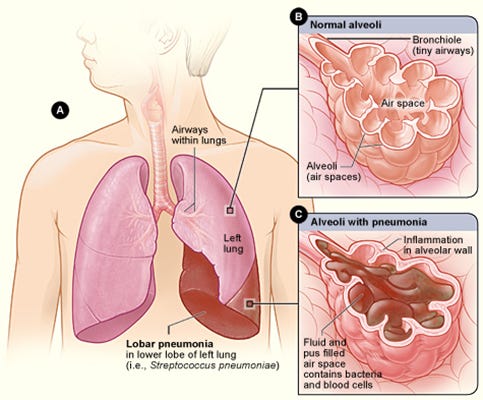
Pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs, which can fill with fluid or pus, making breathing painful and reducing oxygen intake. The severity of pneumonia can range from mild to life-threatening and it can be caused by various pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
An infection known as pneumonia results in inflammation of one or both lung air sacs, which can then fill with pus or fluid and cause pain when breathing and a decrease in oxygen intake. Numerous infections, including viruses like influenza, fungi, and bacteria like Streptococcus pneumoniae, can cause it.
Cough, fever, shortness of breath, and chest pain are typical symptoms. Risk factors include smoking, being extremely old, having long-term medical issues, and having a compromised immune system. Treatment for pneumonia is based on the cause and can include supportive care when necessary, antiviral drugs for viral pneumonia, antibiotics for bacterial pneumonia, and chest X-rays as well as possible blood or sputum testing. For additional details about pneumonia, such as its signs, causes, risk factors, and available treatments
Sources:
Mayo Clinic: Provides detailed information on pneumonia, including its symptoms, causes, risk factors, and treatment options. For comprehensive insights, visit their page on pneumonia: Mayo Clinic Pneumonia Overview.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): Offers a thorough overview of pneumonia, including prevention strategies, diagnosis, and treatment. For detailed information, check out: CDC Pneumonia.
Written by Darshana Srivatsan from MEDILOQUY