Lung Cancer
Written by Darshana Srivatsan
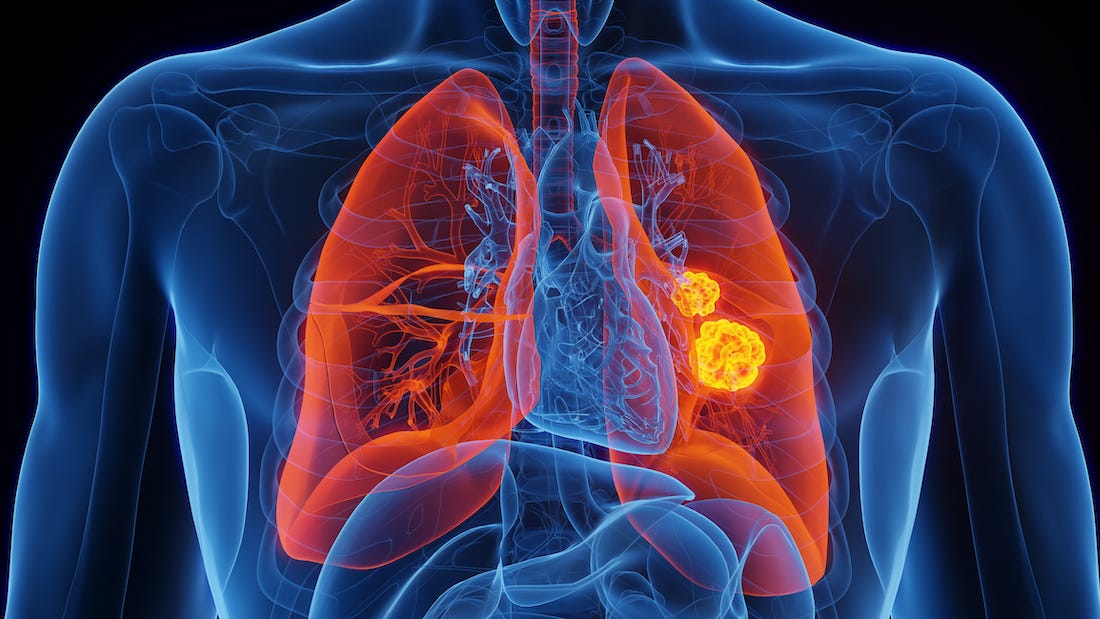
Lung cancer is a type of cancer that starts in the lungs. When a person has lung cancer, abnormal cells in the lungs grow uncontrollably and form tumors. These tumors can interfere with the functioning of the lungs, making it difficult for the person to breathe properly. A chronic cough, blood in the cough, chest pain, dyspnea, exhaustion, inexplicable weight loss, and recurring respiratory infections are typical signs of lung cancer. Chest pain that becomes more pronounced with deep breathing, coughing, or laughing is another symptom to watch for. Shortness of breath can occur, making it difficult to perform everyday activities without feeling winded.
Fatigue and unexplained weight loss are also common, as the body uses more energy to fight the disease. Additionally, recurrent respiratory infections like bronchitis or pneumonia may be a sign, especially if they happen frequently. If you or someone you know experiences these symptoms, it is crucial to seek medical advice for proper diagnosis and treatment. If any of these symptoms exist, you must get medical help, especially if you smoke or have ever smoked. Treatment options for lung cancer depend on the type and stage of cancer but may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, or immunotherapy. Early detection and treatment are crucial for better outcomes in lung cancer.
References
"Bronchial Cancer Symptoms." American Cancer Society, www.cancer.org/cancer/lung-cancer/symptoms.html. Accessed 10 Aug. 2024.
"Symptoms and Diagnosis of Lung Cancer." National Cancer Institute, www.cancer.gov/types/lung/patient/lung-treatment-pdq. Accessed 10 Aug. 2024.
"Symptoms of Lung Cancer." Mayo Clinic, www.mayoclinic.org/diseasesconditions/lung-cancer/symptoms-causes/syc-20351244. Accessed 10 Aug. 2024.
"Understanding Lung Cancer." American Lung Association, www.lung.org/lung-health-diseases/lung-disease-lookup/lung-cancer. Accessed 10 Aug. 2024.