Klinefelter Syndrome
Written by Shrishti Harish
Introduction
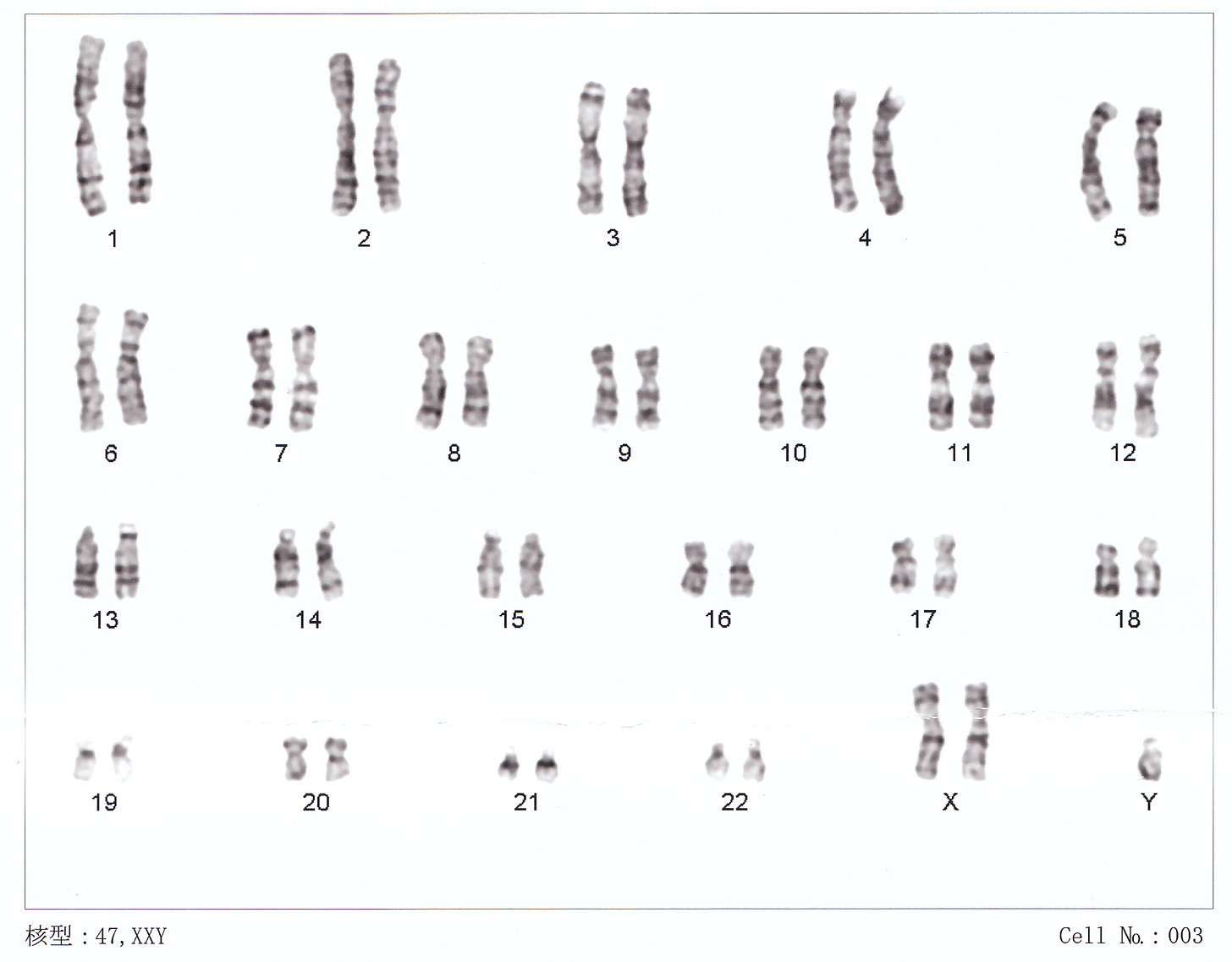
Klinefelter syndrome is a genetic disorder in which a male is born with an extra X chromosome that causes physical and mental abnormalities. It is one of the most common chromosomal disorders and affects 1 in 500 newborn males. Those with Klinefelter syndrome have a total of 47 chromosomes (XXY). With that being said, it is important to note that it is a congenital condition meaning that a person is born with it.
Causes
Klinefelter syndrome occurs when an extra X chromosome is in one’s genetic code. It is not a hereditary condition and changes occur before birth. This can happen when cells divide incorrectly during fetal development or when an egg/sperm carries an extra X chromosome. Additionally, it can occur in nondisjunctions. Nondisjunctions happen when the X chromosome fails to separate properly during the division of reproductive cells.
Symptoms
Enlarged breast tissue (gynecomastia)
Small penis
Small, firm testicles
Weak bones
Low sperm count or no sperm
Infertility
Decreased facial and body hair
Increased body fat
Complications
Klinefelter syndrome can lead to a wide range of complications affecting physical, developmental, and reproductive health. Males diagnosed with KS are usually infertile due to low testosterone levels and reduced sperm production. They also experience learning difficulties and problems with language and social skills. Physical complications include taller-than-average height, reduced muscle mass, and obesity. Additionally, those with Klinefelter syndrome are at high risk for health issues such as osteoporosis, autoimmune disorders, breast cancer, and lung disease.
Diagnosis
Healthcare professionals usually don’t test for Klinefelter syndrome during fetal development. However, if they do, either chromosome analysis or chorionic villus sampling is performed. Chromosome analysis or what is commonly referred to as Karyotype analysis is a test used to confirm a diagnosis of KS. A blood sample is sent to a pathologist to check the shape and look for any abnormalities in the # of chromosomes. Chorionic Villus Sampling is a prenatal test in which small samples of cells from the placenta are extracted to analyze the fetal chromosomes for genetic abnormalities. If not diagnosed during fetal development, healthcare providers will conduct hormone testing. Blood and urine samples are taken to examine if there are abnormal hormone levels.
Treatment
Common treatments include testosterone treatment therapy, breast tissue removal, and speech therapy. Testosterone treatment therapy involves a series of injections, pellets, or gels administered to bring testosterone levels back to normal. It can help grow facial and body hair, improve bone density, and increase muscle mass. Breast tissue removal is performed when males have developed enlarged breasts and excess breast tissue is removed to have a normal-looking chest. Lastly, speech therapy involves targeted exercises to improve communication skills and enhance social interaction abilities.
References
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/klinefelter-syndrome/symptoms-causes/syc-20353949
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21116-klinefelter-syndrome
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/klinefelter-syndrome/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20353954
Written by Shrishti Harish from MEDILOQUY