Invasive Lobular Carcinoma
Written by Shrishti Harish
Introduction
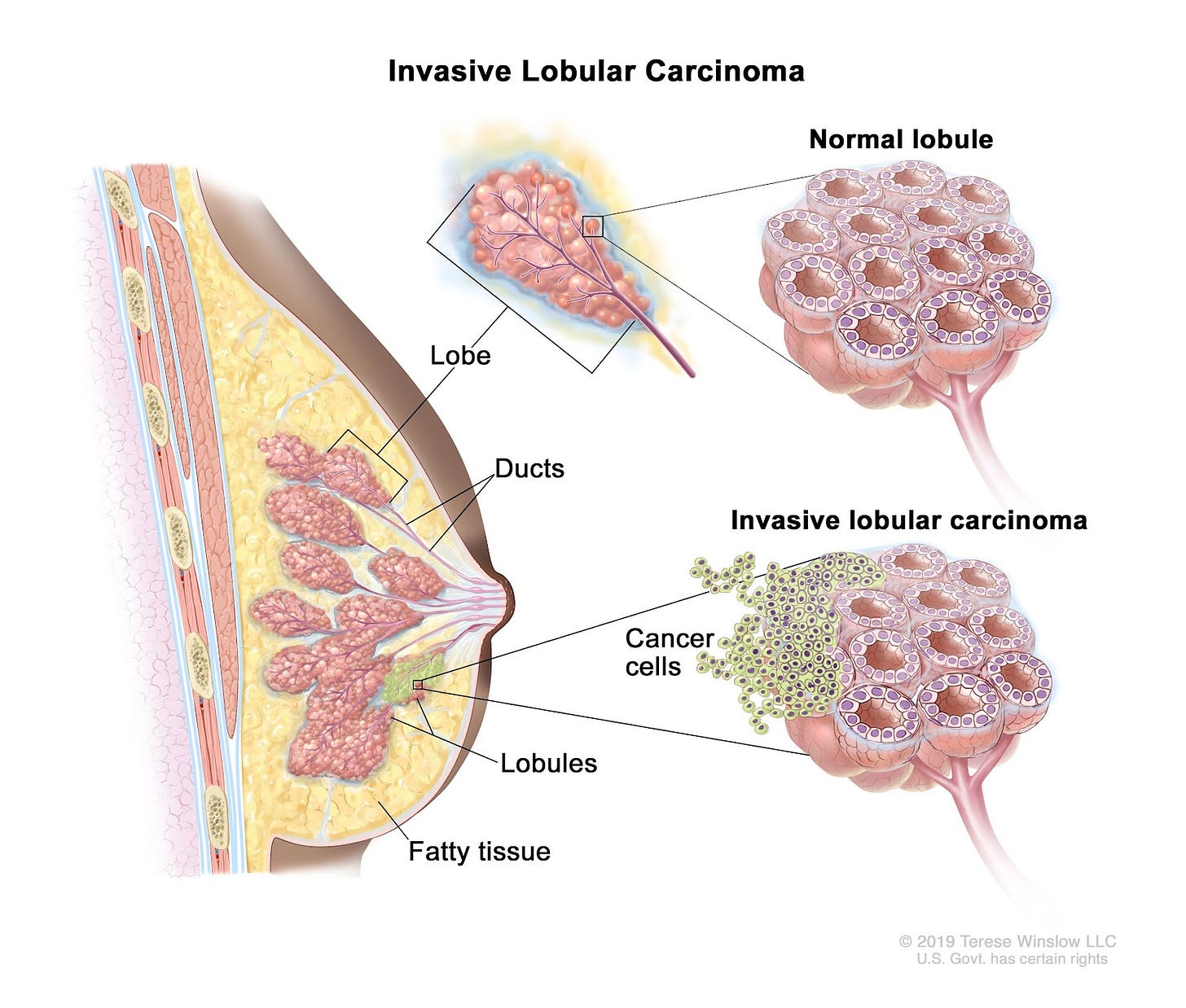
Invasive Lobular Carcinoma which is colloquially referred to as Lobular Breast Cancer is a type of breast cancer that starts in the milk-producing glands of the breast. This is an invasive cancer, meaning that the growth of cells is not only secluded to the lobules but can spread into the breast tissue. It is one the second most common type of breast cancer after invasive ductal carcinoma.
Causes
The exact causes of ILC are not fully understood, but several factors can contribute to its development. Genetic mutations, such as changes in the CDH1, BRCA1, and BRCA2 genes, can increase the risk. Additionally, people who use hormonal therapy after menopause are at an increased risk of developing ILC. A family history of breast cancer puts an individual at higher risk of developing lobular breast cancer, indicating a hereditary component to the disease. Lifestyle choices, such as alcohol consumption, obesity, and lack of physical activity, contribute to the risk, as does previous radiation therapy to the chest area for other cancers. Although everyone is born with breast tissue, women are much more likely than men to get breast cancer.
Symptoms
Newly inverted nipple.
Change in texture/appearance of skin over the breast, such as dimpling.
Nipple discharge.
Lump near armpits.
Diagnosis
Healthcare providers diagnose lobular breast cancer through several steps. It begins with a physical examination, useful for checking lumps or unusual changes in breast tissue. Imaging tests, such as mammograms, ultrasound, and MRI scans are used to capture detailed images of the breast. If these tests indicate abnormalities, a biopsy is performed to confirm the cancer is present. Additionally, healthcare providers take a small sample of breast tissue and send it to a pathology lab for analysis. The pathologists then examine the sample and identify the specific type of breast cancer and its characteristics.
Treatment
Common treatments include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapy. Surgery is usually the first line of treatment for lobular cancer. Surgeons perform either a lumpectomy or mastectomy to remove the tumor. Radiation therapy involves focusing high-energy radiation rays at the breast, and underarm regions to destroy any remaining cancer cells after surgery. Chemotherapy is a treatment that focuses on using drugs to kill cancer cells. Lastly, targeted therapy targets certain characteristics of cancer cells to destroy them.
References
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21180-lobular-breast-cancer
Written by Shrishti Harish from MEDILOQUY