Glioblastoma
Written by Nidhi Kulkarni
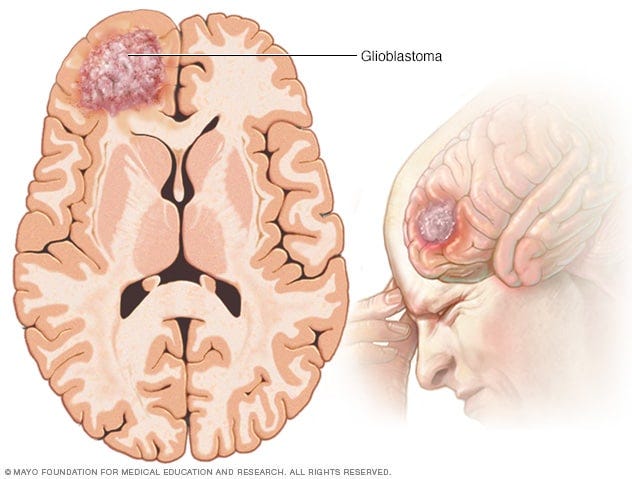
Glioblastomas are stage 4 cancers located in the brain and the spinal cord. These tumors can grow rapidly and destroy healthy cells and brain tissue.
This condition is more common in older adults, and includes symptoms such as:
throbbing headaches
nausea/vomiting
blurry vision
trouble speaking
altered sense of touch and smell
seizures
decline in brain functioning- problems with understanding information
muscle weakness
poor balance and coordination
The direct causes of glioblastomas are unknown, however what scientists do have a proficient understanding of is how they develop. Glioblastomas develop through mutations in brain cell’s DNA structure and instructions. Normal, healthy sets of cells are given instructions to mature at the same rate and die off at the same rate. However, cancer cells affected by glioblastomas multiply at faster rates. This causes cancer cells to stay healthy while the healthy cells die off. The cancer cells then form a mass commonly known as a tumor, which can cause complications and decreased function of the brain.
Treatment starts with surgery, which serves multiple purposes: obtaining tissue samples for biopsy and removing as much of the tumor as possible. For areas where surgery is not possible, Laser Interstitial Thermal Therapy (LITT) may be considered. After having surgery, any remaining tumor is targeted through radiation and chemotherapy. Tumor Treating Fields (TTFields), which interfere with cell division, may also be combined with chemotherapy. Additionally, targeted tile brachytherapy, where radioactive collagen tiles are placed in or near the tumor cavity during surgery, can be an option.
References
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/glioblastoma/symptoms-causes/syc-20569077#:~:text=Glioblastoma%20is%20a%20type%20of%20cancer%20that%20starts%20as%20a,astrocytes%20that%20support%20nerve%20cells.
https://www.abta.org/tumor_types/glioblastoma-gbm/
Written by Nidhi Kulkarni from MEDILOQUY