What is Thrombosis?
Written By Devika Chauhan
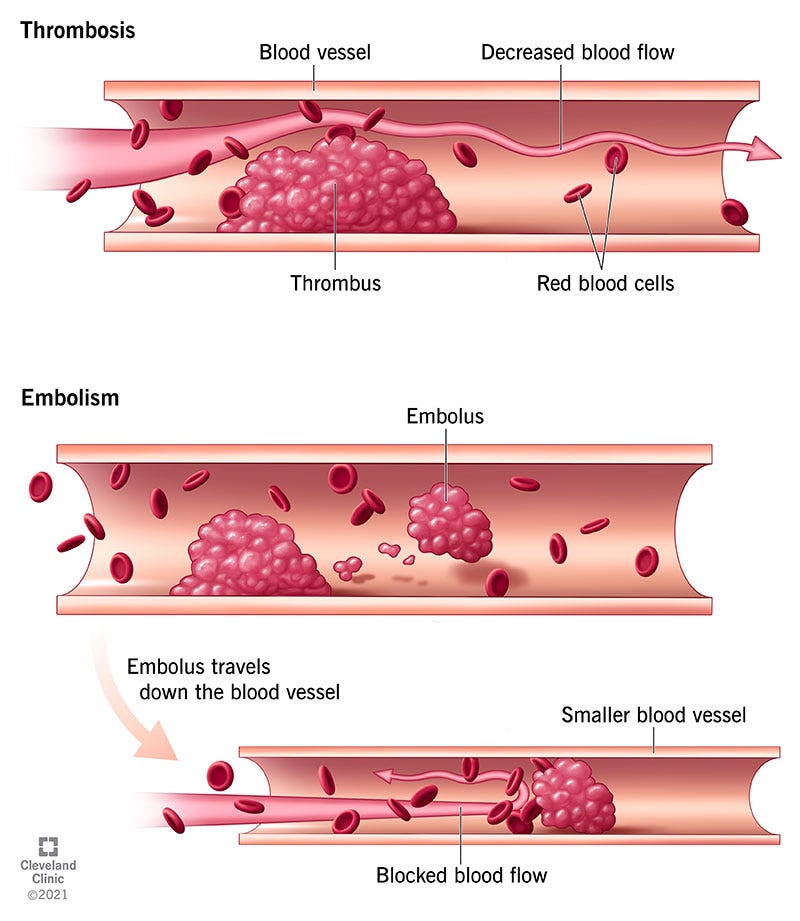
Another, serious condition to add to your dictionary of medical diseases: thrombosis. To elaborate, thrombosis is the formation of blood clots (thrombus) within blood vessels or a chamber of the heart. This disease is caused when the inner lining of blood vessels, endothelium, becomes damaged, or the sudden reduction of blood flow. Both scenarios cause blood to “stick together” creating a lump. Different medical conditions, drugs, medications and other risk factors can increase the susceptibility of blood to form these lumps or even fail to dissolve when needed to. In turn, if not prevented, these clumps can possibly grow and get bigger. Adding on, the clot may even break apart and become an embolus. The embolus can then travel down the blood vessel potentially forming another blockage at a smaller blood vessel (embolism). Blockage of blood prohibits the efficient and adequate transportation of essential nutrients, cells and gas exchange which can diminish the function of vital organs.
There are 2 main types of thrombosis:
Arterial Thrombosis - where blood clots are formed in an artery. This is the most common cause for heart attacks and strokes. Arterial thrombosis can also be caused by a similar disease, atherosclerosis, in which fatty material called plague can build up along the wall of an artery restricting the flow of blood.
Venous Thrombosis - where blood clots are formed in a vein. This is the most common cause for pulmonary embolism, which refers to blood clots in the lungs.
Figure 1: Cleveland Clinic (2023, March 10). Thrombosis Thrombosis: Symptoms & Treatment (clevelandclinic.org)
Thrombectomy is a common type of surgery executed to remove blood clots from clogged blood vessels. Thrombectomy is done by making small incisions on a blood vessel and removing the clot, or by injecting an inflatable balloon into the vessel. This process allows proper blood flow to resume around the body, so that vital organs such as the brain and lungs, can receive a sufficient amount of blood and its nutrients continuously.
In order to detect thrombosis early, it is crucial to take imaging tests such as computed tomography (CT) scans and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans, as well as blood tests regularly. These measures are even more important to follow if one is considered part of the at risk population. However, by abiding by specific medications prescribed by the doctor, for example; cholesterol-lowering, blood pressure and blood thinning medications, the risk of thrombosis can be reduced. Equally importantly, effectively managing diet and exercise proportions by eating a well balanced meal and embedding physical activity in daily lives, the perils of cardiovascular diseases will surely begin to fade away.
References:
Cleveland Clinic. (2023, March 10). Thrombosis: Types, causes, symptoms & treatment. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/22242-thrombosis
Written By Devika Chauhan from MEDILOQUY